Swift Storage
OpenStack Swift Object Storage (Swift) is somewhere we can use to store large static files. It's not particularly convenient, but it is simple and cheap.
How to use Swift on NERC is described here:
https://nerc-project.github.io/nerc-docs/openstack/persistent-storage/object-storage/
My recommendation is to use rclone.
Tips and Tricks
Application Credentials
Following the official documentation section
"Configuring the AWS CLI"
tells you to obtain EC2_ACCESS_KEY and EC2_SECRET_KEY from "Project / API Access"
which is inconvenient because the login is only valid for about a day.
You can obtain credentials which are valid for a year by creating application credentials.
In the top bar click "Identity", then slightly below choose the tab "Application Credentials".
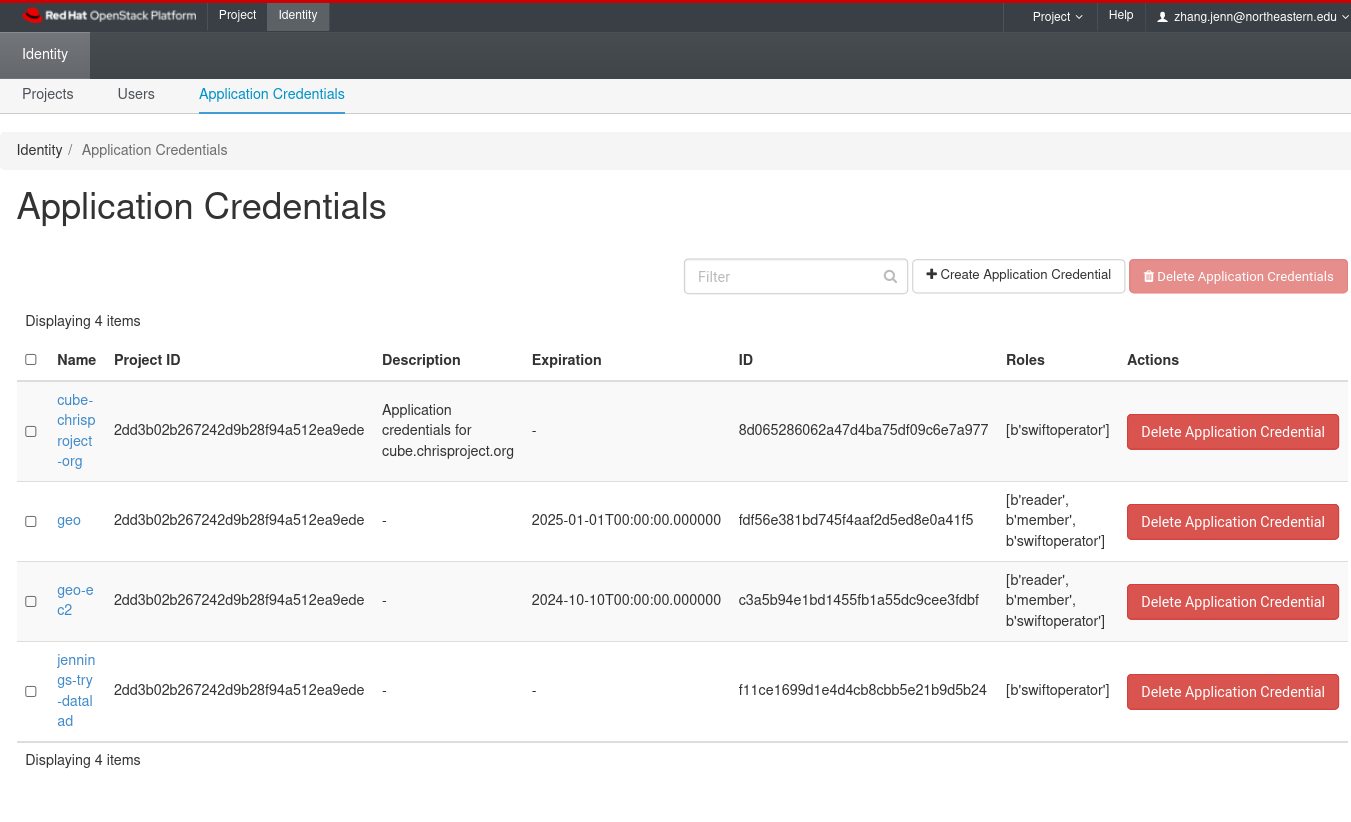
Click "Create Application Credential". Be sure to specify an expiration date to sometime far in the future.
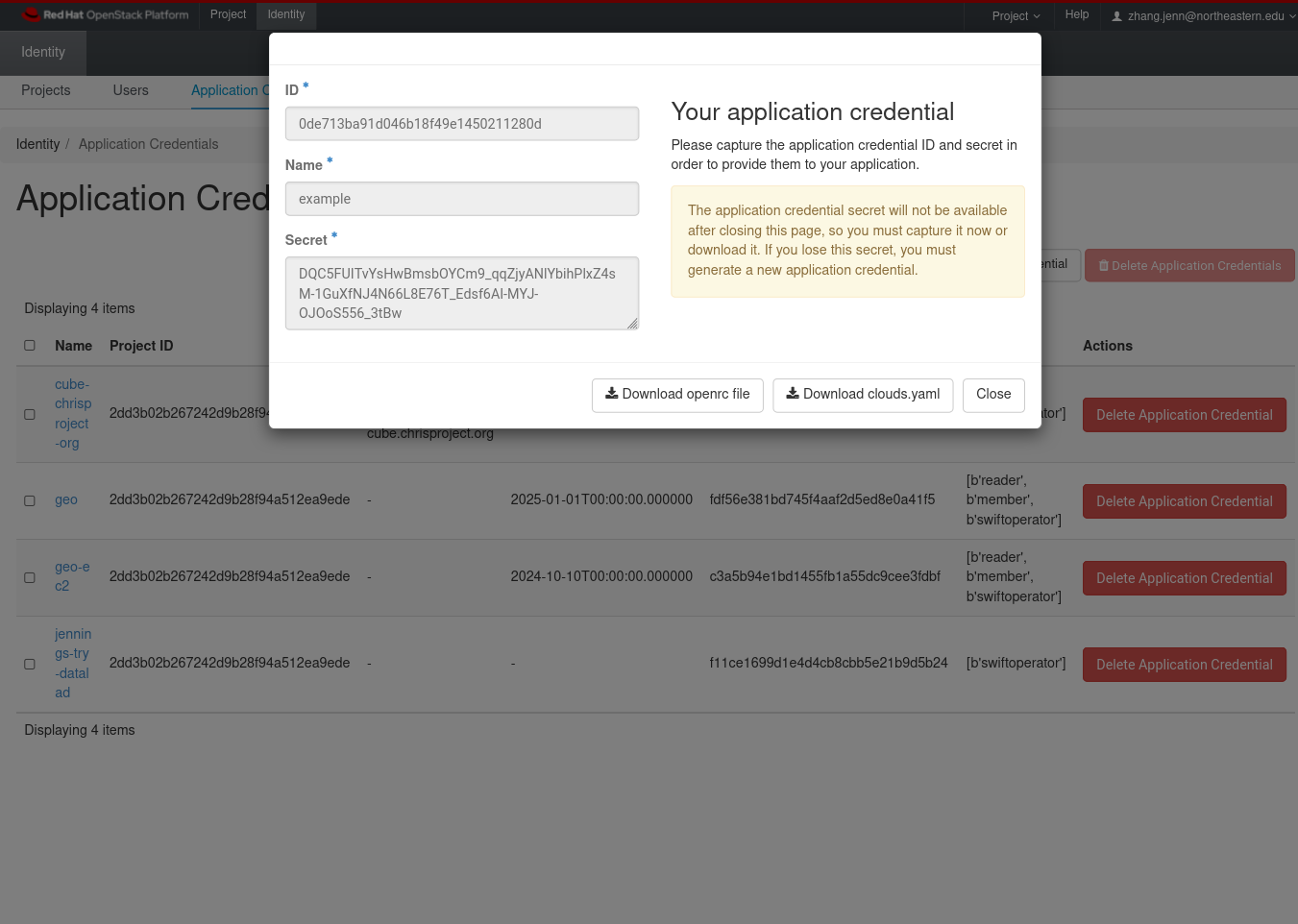
Choose the option "Download openrc file".
Suppose you saved the file as app-cred-example-openrc.sh. In a terminal, run source app-cred-example-openrc.sh.
Then you will be able to run openstack CLI commands.
Create A new EC2_ACCESS_KEY and EC2_SECRET_KEY pair
openstack ec2 credentials create
List existing EC2 credentials
openstack ec2 credentials list
The "Access" and "Secret" can be used to configure rclone as described in the section
"Configuring rclone"
Public Access
The storage_url of Swift can be found here as "Object Store":
https://stack.nerc.mghpcc.org/dashboard/project/api_access/
Alternatively, you can get it from the swift auth command:
eval "$(swift auth)"
echo "$OS_STORAGE_URL"
I have a public container called fnndsc-public. A plaintext list of its contents can be obtained from the URL
https://stack.nerc.mghpcc.org:13808/swift/v1/AUTH_2dd3b02b267242d9b28f94a512ea9ede/fnndsc-public/
To download a specific file from a public bucket, you need to join the container's URL with
the name of the file. For example, the file presentations/jennings.zhang/2018_mcin_fetal_pipeline.pdf
in the fnndsc-public bucket can be downloaded from
https://stack.nerc.mghpcc.org:13808/swift/v1/AUTH_2dd3b02b267242d9b28f94a512ea9ede/fnndsc-public/presentations/jennings.zhang/2018_mcin_fetal_pipeline.pdf
Downloading a Directory
Suppose you want to download an entire directory from a public container. The file list to download can be obtained by running
curl -sf https://stack.nerc.mghpcc.org:13808/swift/v1/AUTH_2dd3b02b267242d9b28f94a512ea9ede/fnndsc-public/ \
| grep '^meetings/recordings/BU_EC528/.*[^/]$'
Breaking it down:
curlfetches a list of the entire contents of the public containerfnndsc-publicgrep '^meetings/recordings/BU_EC528/.*[^/]$'selects only the files in the foldermeetings/recordings/BU_EC528/, excluding directories.
I recommend using GNU parallel to download these files in bulk.
Subdirectories need to be created before downloading files using curl.
For example:
PUBLIC_URL='https://stack.nerc.mghpcc.org:13808/swift/v1/AUTH_2dd3b02b267242d9b28f94a512ea9ede/fnndsc-public/'
directory='meetings/recordings/BU_EC528'
curl -sf "$PUBLIC_URL" \
| grep "^$directory/.*[^/]\$" \
| parallel -j4 --bar "mkdir -p '{//}' && curl -sfo '{}' '$PUBLIC_URL{}'"